Last modified on 01 Oct 2021.
What & Why?
To check the similar distribution of 2 samples drawn from population. If these samples are normal, we can use T-test, but if they are not normal, we need to use KS-test. KS-test is a non-parametric test.
Null hypothesis (): “Two samples drawn from population with the same distribution.”
👉 Read more about p-value. We use this value to evaluate the true/false of above null hypothesis.
The difference (in use) of T-test (need an assumption of nomality) and KS-test (don’t need),
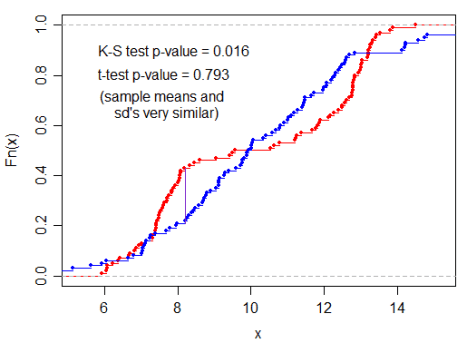
- Two samples have the same mean & standard deviation ⇒ p-value is high ⇒ cannot reject (not true)
- KS-test can detect the variance ⇒ p-value is low ⇒ we can reject ⇒ 2 samples are not the same distribution!!! (yep!)
How?
If the KS statistic is small or the p-value is high, then we cannot reject the hypothesis that the distributions of the two samples are the same.
Code?
from scipy import stats
# one-sample KS test
stats.kstest(x, 'norm')
# two-sample KS test
stats.ks_2samp(x, y)
References
- Matthew E. Clapham – 10: Kolmogorov-Smirnov test (video)
- An example of why we need to use EMD instead of Kolmogorov–Smirnov distance (video).
•Notes with this notation aren't good enough. They are being updated. If you can see this, you are so smart. ;)