Last modified on 01 Oct 2021.
Hierarchical Data Format (HDF)
- Designed to store and organize large amounts of data.
- Store multiple data files in a single data file!
- Different types of information.
- Self describing (metadata included in the file)
- Properties[ref]
:
- Datasets (numpy arrays): fast slicing, compression.
- Group (dictionaries): nesting, POSIX path syntax.
- Attributrs (metadata): datasets/group, key-value.
- HDF5 is row based and really effient than csv for very large file size[ref] .
- Extensions:
.h5,.hdf,.hdf4, … - Tool: HDFView
- Example[ref] :
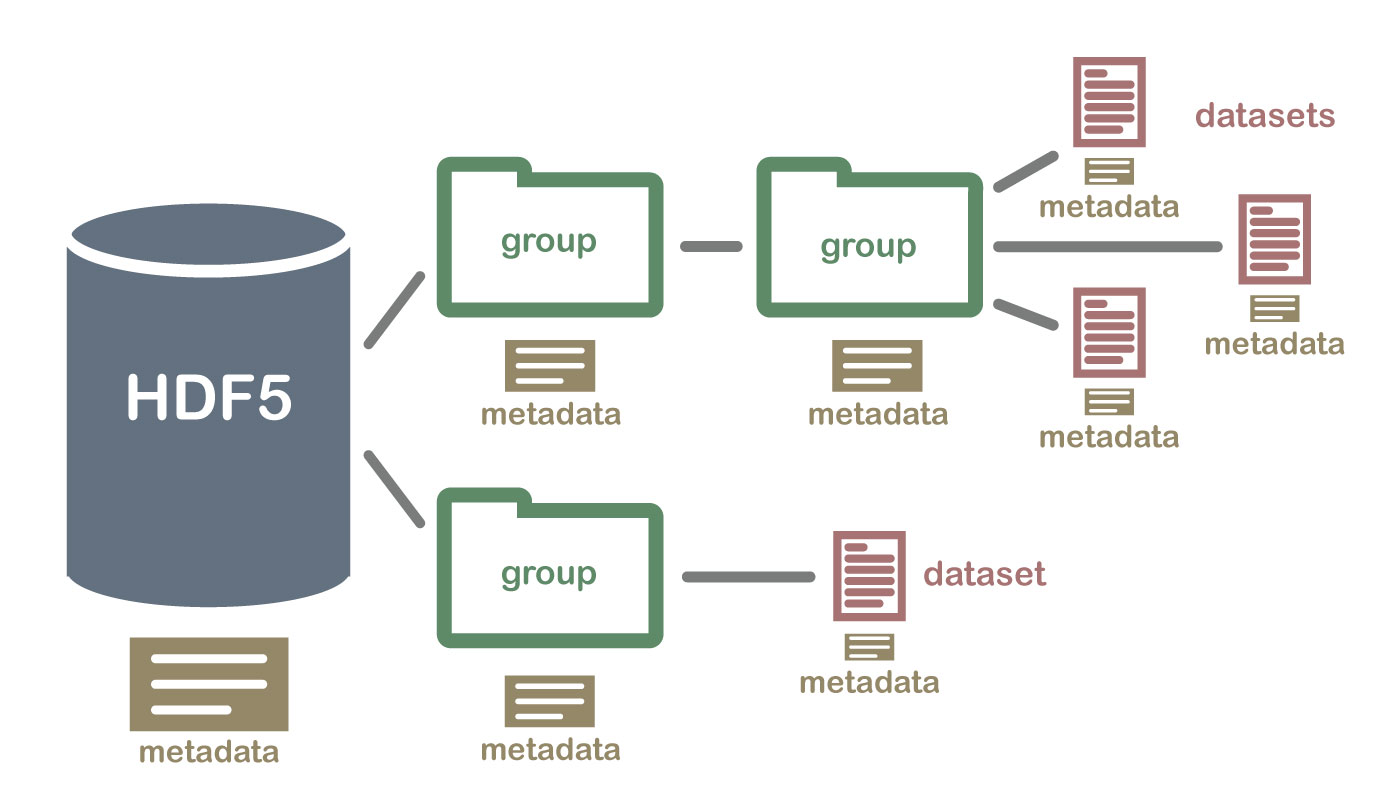 An example HDF5 file structure which contains groups, datasets and associated metadata.
An example HDF5 file structure which contains groups, datasets and associated metadata.
import h5py
f = h5py.File('mytestfile.hdf5', 'r') # read a file
# h5py.File acts like Python dict
dset = f['mydataset']
dset.attrs # attribute
t-digest
later
•Notes with this notation aren't good enough. They are being updated. If you can see this, you are so smart. ;)