Last modified on 01 Oct 2021.
Temporary file and directory
Using tempfile. A file/directory will be created to work. Close files, files are deleted!
import tempfile
# create tmp file and write some data
fp = tempfile.TemporaryFile()
fp.write(b'Hello world!')
# read data from file
fp.seek(0)
fp.read()
# close the file, it'll be removed!
fp.close()
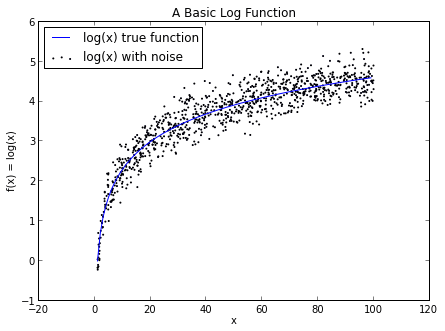
Create some fake data w.r.t. a function
# f(x) = log(x)
import numpy as np
x = np.random.uniform(1, 100, 1000)
y = np.log(x) + np.random.normal(0, .3, 1000)
plt.plot(x,y, '.')
plt.plot(x, np.log(x), '.')
Time Series data
Simple range of time
Read more about date_range(), there are other options, for example, adding timezones.
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df = dict({
'date': pd.date_range('1/1/2020', periods=4, freq='T', tz='Europe/Paris'),
'val1': np.arange(10,10+per,1),
'var2': np.arange(20,20+per,1),
'var3': np.arange(30,30+per,1)
})
df = pd.DataFrame(df)
| date | val1 | var2 | var3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2020-01-01 00:00:00+01:00 | 10 | 20 | 30 |
| 1 | 2020-01-01 00:01:00+01:00 | 11 | 21 | 31 |
| 2 | 2020-01-01 00:02:00+01:00 | 12 | 22 | 32 |
| 3 | 2020-01-01 00:03:00+01:00 | 13 | 23 | 33 |
Manually
With timezone (manually)
df = pd.DataFrame({'timestamp': ['2019-01-31T16:47:00+01:00', '2019-01-31T16:48:00+02:00',
'2019-01-31T16:49:00+02:00', '2019-01-31T16:50:00+01:00']})
With time gaps
Different time gaps (time steps),
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from pandas.tseries.frequencies import to_offset
def generate_sample(starting_date, periods=None, gaps=None, freq="1T", n_vars=1):
"""
General a sample time series dataframe with different periods and time steps.
Parameters:
-----------
starting_date: datetime-like, str, int, float
Starting date of the data.
periods: array, list of int
The list of (different) periods to generate.
gaps: array, list of numbers, optional
The list of gaps (between periods).
freq: frequency strings
The most popular time steps.
n_vars: int
Number of columns of variables.
"""
df = pd.DataFrame()
periods = list(periods)
for idx, _ in enumerate(periods):
per = periods[idx]
if gaps is not None:
gaps = list(gaps)
gap = gaps[idx]
starting_date = str(pd.Timestamp(starting_date) + pd.to_timedelta(to_offset(freq))*gap)
else:
starting_date = str(pd.Timestamp(starting_date))
df_tmp = dict({'date': pd.date_range(starting_date, periods=per, freq=freq)})
df_tmp = pd.DataFrame(df_tmp)
df = pd.concat([df, df_tmp], ignore_index=True, sort=False)
starting_date = str(df_tmp.date.iloc[-1])
for i_var in range(n_vars):
df['var'+str(i_var)] = np.arange(i_var*10, i_var*10+sum(periods))
df = df.infer_objects()
return df
df = generate_sample(starting_date='2020-01-01',
periods=[3, 2],
gaps=[0, 5],
freq='1T',
n_vars=5)
| date | var0 | var1 | var2 | var3 | var4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2020-01-01 00:00:00 | 0 | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 |
| 1 | 2020-01-01 00:01:00 | 1 | 11 | 21 | 31 | 41 |
| 2 | 2020-01-01 00:02:00 | 2 | 12 | 22 | 32 | 42 |
| 3 | 2020-01-01 00:07:00 | 3 | 13 | 23 | 33 | 43 |
| 4 | 2020-01-01 00:08:00 | 4 | 14 | 24 | 34 | 44 |
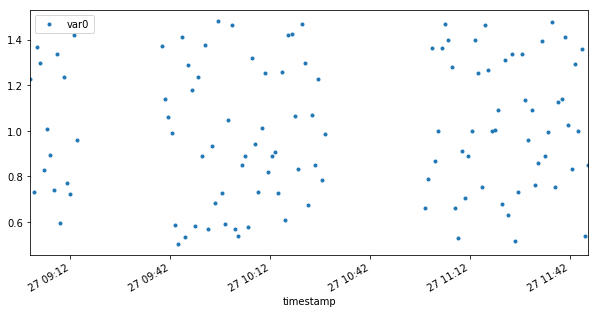
With windows of time
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from pandas.tseries.frequencies import to_offset
def generate_ts_data_window(ts_start='2020-03-27', n_windows=3, n_elements=20, regular=True,
random_seed=None, dif_size=False, gaps='auto', n_point_spec='full', freq='T', n_vars=1):
"""
General a sample time series dataframe with already-shaped windows.
Parameters:
-----------
ts_start: datetime-like, str, int, float
Starting date of the data.
n_windows: int
The number of windows to be generated.
n_elements: int
Max number of elements in each window.
regular: boolean, default=True
The regularity of the distribution in each window.
random_seed: int, default=None
Seed the generator for generating the same data in every test.
If `None`, the choices in `n_elements` (when `dif_size=True`), `regular=True`
are chosen randomly.
dif_size: boolean
Windows with different sizes?
gaps: 'auto' or lst
If 'auto', the gaps between windows are chosen equally.
Otherwise, you have to put the list of percentage (greater than 1) being plus to
`n_elements` (minimum window' size).
Note that, the length of this list is equal to `n_windows-1`.
n_point_spec: 'full' or int, default='full'
The number of points in the special window. If 'full', its number of elements
is generated as others'.
freq: frequency strings, default='T'
The most popular time steps.
n_vars: int
Number of variable columns.
"""
df = pd.DataFrame()
gap = 0
np.random.seed(random_seed)
# choose the special window
spec_win = np.random.randint(0, n_windows)
for w in range(n_windows):
n_elements_new = n_elements
if (n_point_spec != 'full') and (w == spec_win):
n_elements_new = n_point_spec
elif dif_size:
# add randomly more data points
n_elements_new = int(n_elements + np.random.randint(1, 100 + 1)/100*n_elements)
ts_start = str(pd.Timestamp(ts_start) + pd.to_timedelta(to_offset(freq))*gap)
df_tmp = dict({'timestamp': pd.date_range(ts_start, periods=n_elements_new, freq=freq)})
for i_var in range(n_vars):
df_tmp['var'+str(i_var)] = 0.5 + np.random.random_sample((n_elements_new,))
df_tmp = pd.DataFrame(df_tmp)
if not regular:
# remove randomly 0% - 50% data points from a window
frac = 0.5+0.5*np.random.random()
df_tmp = df_tmp.sample(frac=frac, axis=0)
df = pd.concat([df, df_tmp], ignore_index=True, sort=False)
ts_start = str(df_tmp['timestamp'].iloc[-1])
gap = n_elements / 2 # default: gap=50% length of n_elements
if (gaps != 'auto') and (w != n_windows-1):
gap = n_elements / 2 + gaps[w]*n_elements/100
print(gap)
df = df.infer_objects()
return df
df = generate_ts_data_window(n_windows=3,
regular=True,
n_elements=50,
dif_size=False,
n_point_spec=15,
gaps=[1, 10])
df.set_index('timestamp').plot(figsize=(10,5), style='.')
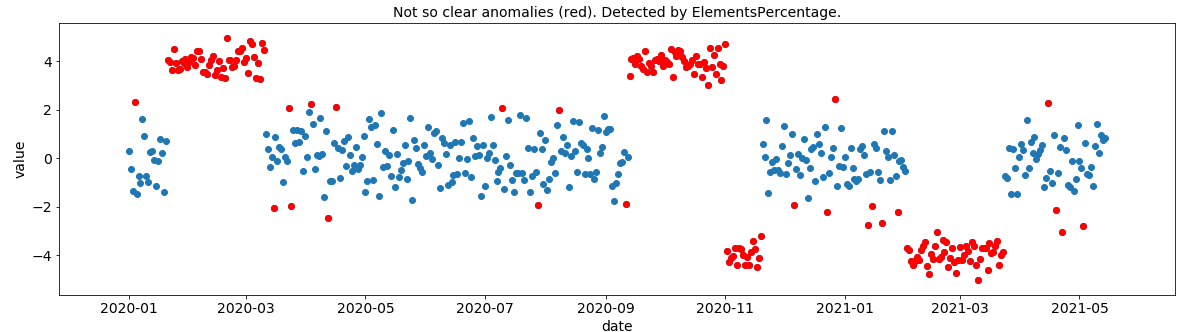
Stationary TS with noise
Random choose the positions of anomal group + random choose the number of points in each group.
# CREATE A SAMPLE OF STATIONARY TIME SERIES
np.random.seed(124)
ts_start = '2020-01-01'
periods = 500
num_group_noise = 4
max_point_each_group_noise = 50
max_noise = 7
date = pd.date_range(ts_start, periods=periods, freq='D')
data = np.random.randn(periods)
# add noises
noise_num_pts = np.random.randint(5,max_point_each_group_noise, (num_group_noise,)) # number of points at each position of noise
noise_pos = np.random.choice(periods, num_group_noise) # number of position having noises
list_of_idx_noise = []
for idx, pos in enumerate(noise_pos):
if periods - pos > max_point_each_group_noise:
# noises = (-1)**(idx)*max_noise + 0.5*np.random.randn(noise_num_pts[idx]) # 2 sides
noises = max_noise + 0.5*np.random.randn(noise_num_pts[idx]) # 1 sides
data[pos:pos+noise_num_pts[idx]] = noises
list_of_idx_noise += [*range(pos, pos+noise_num_pts[idx], 1)]
df = pd.DataFrame({'date': date, 'value': data})
df = df.set_index('date')
list_of_idx_noise = list(set(list_of_idx_noise))
df_out = df.iloc[list_of_idx_noise] # df of noises
# PLOT DATA WITH ANOMALIES
def plot_anomalies(df, df_anomalies=None, idx_anomalies=None, title=None):
if not idx_anomalies:
idx_anomalies = df_anomalies['ts_start'].astype('datetime64[ms]').to_list()
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 5))
plt.scatter(df.index, df.value)
plt.scatter(idx_anomalies, df.loc[idx_anomalies], c='r')
plt.xticks(fontsize=14)
plt.yticks(fontsize=14)
plt.xlabel('date', fontsize=14)
plt.ylabel('value', fontsize=14)
if title:
plt.title(title, fontsize=14)